
At least compare the fingerprints, so you can be sure you trust the right certificate. But you're trusting the network in this case. DER encoded binary X.509 (.CER).Īnother way to get the certificate is to follow steps 6 to 10 on your client computer, on the Remote Desktop warning dialog mentioned in the question. There should be a single certificate with your computer's name.
Select Certificates (Local Computer) -> Remote Desktop -> Certificates. The console should now contain Certificates (Local Computer). Select Certificates -> Add > -> Computer account -> Local computer -> Finish. If you think you already installed the certificate, skip to "Move Certificate on Client." Export Certificate on Serverįirst the certificate needs to be exported to a file. Adding it to the user's "Trusted Root Certification Authorities" store is not enough! If this sounds confusing don't worry - it is. 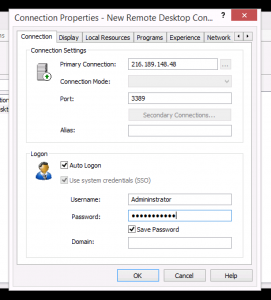 Create a DWORD named fClientDisableUDP and assign it a value of 1.The certificate needs to be added to your Local Computer's "Trusted Root Certification Authorities" store. Navigate to HKLM\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows NT\Terminal Services\Client. The fix is to disable UDP on the client workstation: It requires a registry change, so all the usual warnings and caveats apply here, back it up first! Consult this Microsoft support article for more information. The research in this solution hint that this is caused only when going through a VPN, others mention that it occurs only on Windows 8 paired with a Gateway server, but it has worked for many of our users. Click on Disable to disable the UDP Settings. Click on Tools – More Tools – Local RDP/RemoteApp Manager. Open Remote Desktop Manager as an administrator. There's an option in RDM to disable UDP usage. Load plug-ins in embedded mode Solution for UDP usage
Create a DWORD named fClientDisableUDP and assign it a value of 1.The certificate needs to be added to your Local Computer's "Trusted Root Certification Authorities" store. Navigate to HKLM\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows NT\Terminal Services\Client. The fix is to disable UDP on the client workstation: It requires a registry change, so all the usual warnings and caveats apply here, back it up first! Consult this Microsoft support article for more information. The research in this solution hint that this is caused only when going through a VPN, others mention that it occurs only on Windows 8 paired with a Gateway server, but it has worked for many of our users. Click on Disable to disable the UDP Settings. Click on Tools – More Tools – Local RDP/RemoteApp Manager. Open Remote Desktop Manager as an administrator. There's an option in RDM to disable UDP usage. Load plug-ins in embedded mode Solution for UDP usage 
Go in the Experience tab of your RDP sessions and set Load plug-ins in embedded mode to No.

The two causes are RDP plug-ins and UDP usage under certain conditions. The fix is to disable UDP on the client workstation:.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
